StreamLines#
Qualified name: manim.mobject.vector\_field.StreamLines
- class StreamLines(func, color=None, color_scheme=None, min_color_scheme_value=0, max_color_scheme_value=2, colors=[ManimColor('#236B8E'), ManimColor('#83C167'), ManimColor('#FFFF00'), ManimColor('#FC6255')], x_range=None, y_range=None, z_range=None, three_dimensions=False, noise_factor=None, n_repeats=1, dt=0.05, virtual_time=3, max_anchors_per_line=100, padding=3, stroke_width=1, opacity=1, **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
VectorFieldStreamLines represent the flow of a
VectorFieldusing the trace of moving agents.Vector fields are always based on a function defining the vector at every position. The values of this functions is displayed by moving many agents along the vector field and showing their trace.
- Parameters:
func (Callable[[np.ndarray], np.ndarray]) – The function defining the rate of change at every position of the vector field.
color (ParsableManimColor | None) – The color of the vector field. If set, position-specific coloring is disabled.
color_scheme (Callable[[np.ndarray], float] | None) – A function mapping a vector to a single value. This value gives the position in the color gradient defined using min_color_scheme_value, max_color_scheme_value and colors.
min_color_scheme_value (float) – The value of the color_scheme function to be mapped to the first color in colors. Lower values also result in the first color of the gradient.
max_color_scheme_value (float) – The value of the color_scheme function to be mapped to the last color in colors. Higher values also result in the last color of the gradient.
colors (Sequence[ParsableManimColor]) – The colors defining the color gradient of the vector field.
x_range (Sequence[float]) – A sequence of x_min, x_max, delta_x
y_range (Sequence[float]) – A sequence of y_min, y_max, delta_y
z_range (Sequence[float]) – A sequence of z_min, z_max, delta_z
three_dimensions (bool) – Enables three_dimensions. Default set to False, automatically turns True if z_range is not None.
noise_factor (float | None) – The amount by which the starting position of each agent is altered along each axis. Defaults to
delta_y / 2if not defined.n_repeats – The number of agents generated at each starting point.
dt – The factor by which the distance an agent moves per step is stretched. Lower values result in a better approximation of the trajectories in the vector field.
virtual_time – The time the agents get to move in the vector field. Higher values therefore result in longer stream lines. However, this whole time gets simulated upon creation.
max_anchors_per_line – The maximum number of anchors per line. Lines with more anchors get reduced in complexity, not in length.
padding – The distance agents can move out of the generation area before being terminated.
stroke_width – The stroke with of the stream lines.
opacity – The opacity of the stream lines.
Examples
Example: BasicUsage ¶
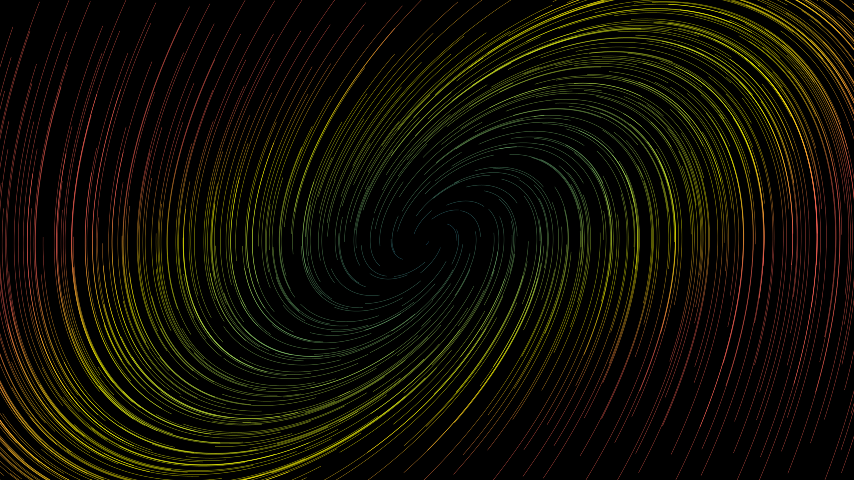
from manim import * class BasicUsage(Scene): def construct(self): func = lambda pos: ((pos[0] * UR + pos[1] * LEFT) - pos) / 3 self.add(StreamLines(func))
class BasicUsage(Scene): def construct(self): func = lambda pos: ((pos[0] * UR + pos[1] * LEFT) - pos) / 3 self.add(StreamLines(func))Example: SpawningAndFlowingArea ¶
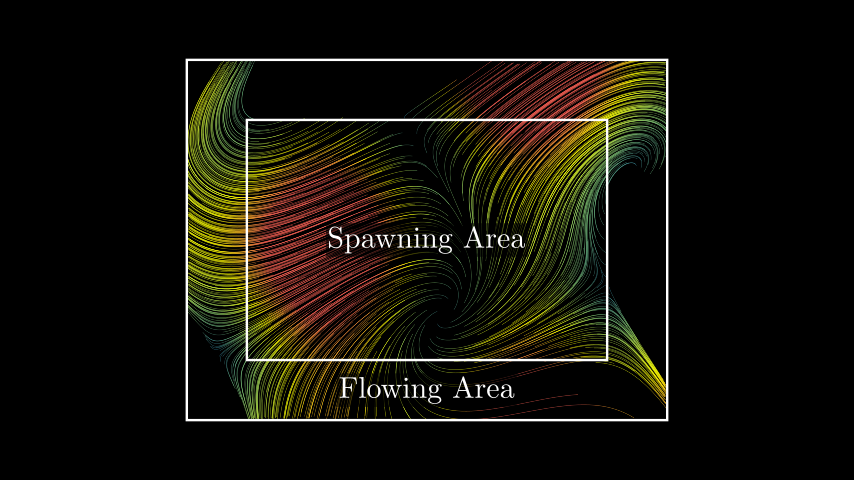
from manim import * class SpawningAndFlowingArea(Scene): def construct(self): func = lambda pos: np.sin(pos[0]) * UR + np.cos(pos[1]) * LEFT + pos / 5 stream_lines = StreamLines( func, x_range=[-3, 3, 0.2], y_range=[-2, 2, 0.2], padding=1 ) spawning_area = Rectangle(width=6, height=4) flowing_area = Rectangle(width=8, height=6) labels = [Tex("Spawning Area"), Tex("Flowing Area").shift(DOWN * 2.5)] for lbl in labels: lbl.add_background_rectangle(opacity=0.6, buff=0.05) self.add(stream_lines, spawning_area, flowing_area, *labels)
class SpawningAndFlowingArea(Scene): def construct(self): func = lambda pos: np.sin(pos[0]) * UR + np.cos(pos[1]) * LEFT + pos / 5 stream_lines = StreamLines( func, x_range=[-3, 3, 0.2], y_range=[-2, 2, 0.2], padding=1 ) spawning_area = Rectangle(width=6, height=4) flowing_area = Rectangle(width=8, height=6) labels = [Tex("Spawning Area"), Tex("Flowing Area").shift(DOWN * 2.5)] for lbl in labels: lbl.add_background_rectangle(opacity=0.6, buff=0.05) self.add(stream_lines, spawning_area, flowing_area, *labels)Methods
The creation animation of the stream lines.
End the stream line animation smoothly.
Animates the stream lines using an updater.
Attributes
animateUsed to animate the application of any method of
self.animation_overridescolordepthThe depth of the mobject.
fill_colorIf there are multiple colors (for gradient) this returns the first one
heightThe height of the mobject.
n_points_per_curvesheen_factorstroke_colorwidthThe width of the mobject.
- _original__init__(func, color=None, color_scheme=None, min_color_scheme_value=0, max_color_scheme_value=2, colors=[ManimColor('#236B8E'), ManimColor('#83C167'), ManimColor('#FFFF00'), ManimColor('#FC6255')], x_range=None, y_range=None, z_range=None, three_dimensions=False, noise_factor=None, n_repeats=1, dt=0.05, virtual_time=3, max_anchors_per_line=100, padding=3, stroke_width=1, opacity=1, **kwargs)#
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
- Parameters:
func (Callable[[ndarray], ndarray]) –
color (Optional[Union[ManimColor, int, str, Tuple[int, int, int], Tuple[float, float, float], Tuple[int, int, int, int], Tuple[float, float, float, float], ndarray[Any, dtype[int64]], ndarray[Any, dtype[float64]]]]) –
color_scheme (Optional[Callable[[ndarray], float]]) –
min_color_scheme_value (float) –
max_color_scheme_value (float) –
colors (Sequence[Union[ManimColor, int, str, Tuple[int, int, int], Tuple[float, float, float], Tuple[int, int, int, int], Tuple[float, float, float, float], ndarray[Any, dtype[int64]], ndarray[Any, dtype[float64]]]]) –
x_range (Sequence[float]) –
y_range (Sequence[float]) –
z_range (Sequence[float]) –
three_dimensions (bool) –
noise_factor (float | None) –
- create(lag_ratio=None, run_time=None, **kwargs)[source]#
The creation animation of the stream lines.
The stream lines appear in random order.
- Parameters:
lag_ratio (float | None) – The lag ratio of the animation. If undefined, it will be selected so that the total animation length is 1.5 times the run time of each stream line creation.
run_time (Optional[Callable[[float], float]]) – The run time of every single stream line creation. The runtime of the whole animation might be longer due to the lag_ratio. If undefined, the virtual time of the stream lines is used as run time.
- Returns:
The creation animation of the stream lines.
- Return type:
Examples
Example: StreamLineCreation ¶
from manim import * class StreamLineCreation(Scene): def construct(self): func = lambda pos: (pos[0] * UR + pos[1] * LEFT) - pos stream_lines = StreamLines( func, color=YELLOW, x_range=[-7, 7, 1], y_range=[-4, 4, 1], stroke_width=3, virtual_time=1, # use shorter lines max_anchors_per_line=5, # better performance with fewer anchors ) self.play(stream_lines.create()) # uses virtual_time as run_time self.wait()
class StreamLineCreation(Scene): def construct(self): func = lambda pos: (pos[0] * UR + pos[1] * LEFT) - pos stream_lines = StreamLines( func, color=YELLOW, x_range=[-7, 7, 1], y_range=[-4, 4, 1], stroke_width=3, virtual_time=1, # use shorter lines max_anchors_per_line=5, # better performance with fewer anchors ) self.play(stream_lines.create()) # uses virtual_time as run_time self.wait()
- end_animation()[source]#
End the stream line animation smoothly.
Returns an animation resulting in fully displayed stream lines without a noticeable cut.
- Returns:
The animation fading out the running stream animation.
- Return type:
- Raises:
ValueError – if no stream line animation is running
Examples
Example: EndAnimation ¶
from manim import * class EndAnimation(Scene): def construct(self): func = lambda pos: np.sin(pos[0] / 2) * UR + np.cos(pos[1] / 2) * LEFT stream_lines = StreamLines( func, stroke_width=3, max_anchors_per_line=5, virtual_time=1, color=BLUE ) self.add(stream_lines) stream_lines.start_animation(warm_up=False, flow_speed=1.5, time_width=0.5) self.wait(1) self.play(stream_lines.end_animation())
class EndAnimation(Scene): def construct(self): func = lambda pos: np.sin(pos[0] / 2) * UR + np.cos(pos[1] / 2) * LEFT stream_lines = StreamLines( func, stroke_width=3, max_anchors_per_line=5, virtual_time=1, color=BLUE ) self.add(stream_lines) stream_lines.start_animation(warm_up=False, flow_speed=1.5, time_width=0.5) self.wait(1) self.play(stream_lines.end_animation())
- start_animation(warm_up=True, flow_speed=1, time_width=0.3, rate_func=<function linear>, line_animation_class=<class 'manim.animation.indication.ShowPassingFlash'>, **kwargs)[source]#
Animates the stream lines using an updater.
The stream lines will continuously flow
- Parameters:
warm_up (bool) – If True the animation is initialized line by line. Otherwise it starts with all lines shown.
flow_speed (float) – At flow_speed=1 the distance the flow moves per second is equal to the magnitude of the vector field along its path. The speed value scales the speed of this flow.
time_width (float) – The proportion of the stream line shown while being animated
rate_func (Callable[[float], float]) – The rate function of each stream line flashing
line_animation_class (type[manim.animation.indication.ShowPassingFlash]) – The animation class being used
- Return type:
None
Examples
Example: ContinuousMotion ¶
from manim import * class ContinuousMotion(Scene): def construct(self): func = lambda pos: np.sin(pos[0] / 2) * UR + np.cos(pos[1] / 2) * LEFT stream_lines = StreamLines(func, stroke_width=3, max_anchors_per_line=30) self.add(stream_lines) stream_lines.start_animation(warm_up=False, flow_speed=1.5) self.wait(stream_lines.virtual_time / stream_lines.flow_speed)
class ContinuousMotion(Scene): def construct(self): func = lambda pos: np.sin(pos[0] / 2) * UR + np.cos(pos[1] / 2) * LEFT stream_lines = StreamLines(func, stroke_width=3, max_anchors_per_line=30) self.add(stream_lines) stream_lines.start_animation(warm_up=False, flow_speed=1.5) self.wait(stream_lines.virtual_time / stream_lines.flow_speed)